BEARCAT Instrumentation Test Engine: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
| (31 dazwischenliegende Versionen von 5 Benutzern werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 2: | Zeile 2: | ||
BEARCAT (for "Banc d’Essai Avancé pour la Recherche en Combustion et Aérothermique des Turbomachines") is a brand new turboshaft developed by SAFRAN-Tech, the R&D Center of the SAFRAN Group. BEARCAT is based on a MAKILA engine, a turboshaft developed by Safran Helicopter Engines (formerly Turboméca) and powering the H215 and the H225 Airbus Helicopters. BEARCAT has been developed in order to perform fine characterization of aero-thermal phenomena occurring within the combustion chamber and the High Pressure Turbine as well as their interactions. Therefore, BEARCAT differs from a standard test engine by the implementation of metrologies, in order to perform both steady and non-steady flow measurements which will be used to validate CFD codes and models. | BEARCAT (for "Banc d’Essai Avancé pour la Recherche en Combustion et Aérothermique des Turbomachines") is a brand new turboshaft developed by SAFRAN-Tech, the R&D Center of the SAFRAN Group. BEARCAT is based on a MAKILA engine, a turboshaft developed by Safran Helicopter Engines (formerly Turboméca) and powering the H215 and the H225 Airbus Helicopters. BEARCAT has been developed in order to perform fine characterization of aero-thermal phenomena occurring within the combustion chamber and the High Pressure Turbine as well as their interactions. Therefore, BEARCAT differs from a standard test engine by the implementation of metrologies, in order to perform both steady and non-steady flow measurements which will be used to validate CFD codes and models. | ||
| − | Therefore, BEARCAT could be used in the framework of fundamental studies, such as aerodynamics, thermics, combustion, acoustics, … as well as applied studies (sensors, materials, technologies, fuels, …). Indeed, thanks to the high degree of instrumentation, BEARCAT allows the fine characterization of the test conditions and then contributes to the TRL enhancement of the tested technology. | + | Therefore, BEARCAT could be used in the framework of fundamental studies, such as aerodynamics, thermics, combustion, acoustics, … as well as applied studies (sensors, materials, technologies, fuels, …). Indeed, thanks to the high degree of instrumentation, BEARCAT allows for the fine characterization of the test conditions and then contributes to the TRL enhancement of the tested technology. |
| − | == BEARCAT: | + | == BEARCAT: A heavily instrumented Turboshaft == |
| − | BEARCAT is based on a MAKILA turboshaft | + | BEARCAT is based on a MAKILA turboshaft. |
| − | The main purpose of BEARCAT is to generate an extensive data base which will be used to validate CFD codes, transient thermal codes, … and models. To address these concerns, it was felt necessary to instrument an engine within the hot temperature | + | The main purpose of BEARCAT is to generate an extensive data base which will be used to validate CFD codes, transient thermal codes, … and models. To address these concerns, it was felt necessary to instrument an engine within the hot temperature / high pressure region, by means of a metrology generally implemented on partial test rig and allowing a fine characterization of local unsteady characteristics of encountered flows. |
| − | The instrumentation implemented on BEARCAT is summarized in table 2. Special | + | The instrumentation implemented on BEARCAT is summarized in table 2. Special attention was given to the characterization of secondary flows and boundary conditions in terms of temperature (mass and flow) and pressure, in order to characterize the machine performances. |
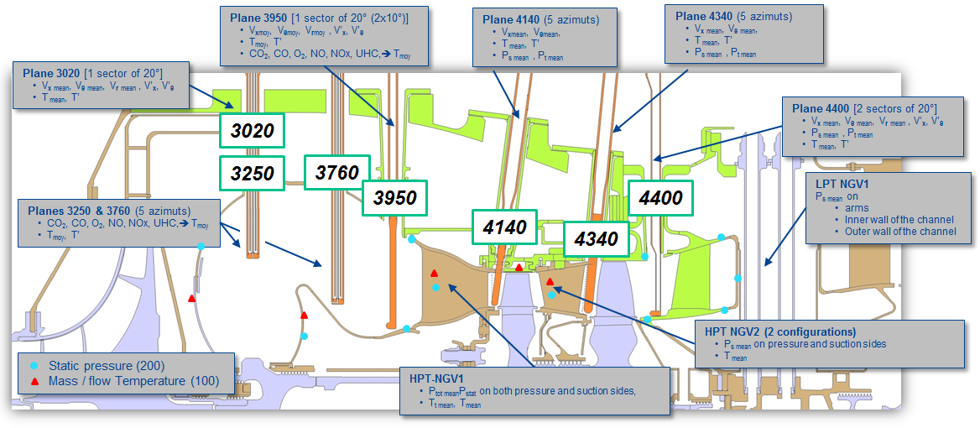
| − | + | On the other hand, the main flow can be investigated by means of probes implemented at 7 sections, from the Combustor inlet to the HP-Turbine outlet. Each section, or plane, has its own respective instrumentation (indicated in figure 2). Note that only one probe can be implemented at a time. | |
| − | The probe is automatically traversed | + | The probe is being automatically traversed into the engine thanks to a versatile device called SYSPAC. This device performs also the data acquisition, independent of the probe type, it performs the data analysis and associates the data to the main engine data collected from the Human Machine Interface. |
=== A perfect tool for fundamental studies === | === A perfect tool for fundamental studies === | ||
| − | Thanks to the implemented instrumentation BEARCAT is really dedicated to fundamental studies. Indeed, BEARCAT allows both steady and non-steady flow measurements (velocity, static or dynamic pressure, temperature, chemical species …) coupled with mass temperature or local stress. A classical metrology allows the determination of detailed performances as well as the fine knowledge of the average experimental conditions generating the investigated flows (collected from the HMI). | + | Thanks to the implemented instrumentation BEARCAT is really dedicated to fundamental studies. Indeed, BEARCAT allows for both steady and non-steady flow measurements (velocity, static or dynamic pressure, temperature, chemical species …) coupled with mass temperature or local stress. A classical metrology allows the determination of detailed performances as well as the fine knowledge of the average experimental conditions generating the investigated flows (collected from the HMI). |
| − | In total, 23 physical access ports es are available on BEARCAT at the level of the | + | In total, 23 physical access ports es are available on BEARCAT at the level of the Combustor and the HP Turbine, allowing the implementation of a wide range of metrologies, yet existing or to be developed. |
=== A technological platform for Technology Readiness Level (TRL) enhancement === | === A technological platform for Technology Readiness Level (TRL) enhancement === | ||
| − | BEARCAT is also well suited | + | BEARCAT is also well suited for TRL enhancement tests with many advantages. BEARCAT is a real engine with a real and well-known engine environment in terms of thermodynamics, mechanics, vibrations, chemistry …. It gives also the opportunity to eventually quantify the impact of the implemented technology: sensors, equipment, material, fuel, design, materials, process, …. by means of the implemented metrology. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Example Images == | == Example Images == | ||
[[Datei:BEARCAT_1.png|micro]] | [[Datei:BEARCAT_1.png|micro]] | ||
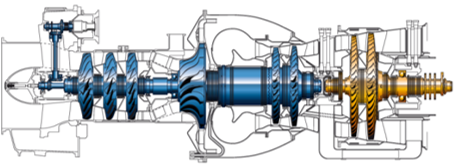
| − | Figure 1: Cross sectional view of a MAKILA 2A1 engine | + | Figure 1: Cross-sectional view of a MAKILA 2A1 engine |
| Zeile 33: | Zeile 31: | ||
[[Datei:BEARCAT_2.png|micro]] | [[Datei:BEARCAT_2.png|micro]] | ||
| − | Figure 2: Partial cross section of BEARCAT showing the instrumentation implementation. | + | Figure 2: Partial cross-section of BEARCAT showing the instrumentation implementation. |
== Location == | == Location == | ||
| − | Tests | + | Tests will be carried out at SAFRAN Group in house facilities in the Safran Helicopter Engine facility located at Bordes F-64510), south of France. |
'''Who the facility will be offered to:''' | '''Who the facility will be offered to:''' | ||
| − | * Sensor manufacturers | + | * Sensor manufacturers : new sensor improvement in realistic conditions. |
| − | + | * Universities interested to validate model, computations on a real turboshaft engine by means of dedicated measurements in the fields of aerodynamics, combustion, acoustics, thermics, ... | |
| − | * Universities | + | * Possibility to work in the Framework of EC Projects. |
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Engines which can be included in the facility == | == Engines which can be included in the facility == | ||
| − | * | + | * The rig and the Instrumentation are devoted to BEARCAT. Nevertheless, we are open to new instrumentation development for which BEARCAT would be used for TRL enhancement in engine representative conditions. |
== Type of modifications to engines == | == Type of modifications to engines == | ||
| − | + | Even any modification of BEARCAT is quickly complicated and expensive, some local modifications in order to implement new type of sensors would be studied very carefully. Don't hesitate to constact us ! | |
== Probe specifications == | == Probe specifications == | ||
A heavily instrumented turboshaft: 385 measurement points. | A heavily instrumented turboshaft: 385 measurement points. | ||
| − | * 7 sections (23 physical access ports), from Combustor inlet to HP | + | * 7 sections (23 physical access ports), from Combustor inlet to HP Turbine outlet, fitted with probes. |
* Both steady and unsteady measurements available. | * Both steady and unsteady measurements available. | ||
* Well suited to fundamental studies such as CFD validation. | * Well suited to fundamental studies such as CFD validation. | ||
* Well suited to technological works such as TRL enhancement on a real turboshaft engine. | * Well suited to technological works such as TRL enhancement on a real turboshaft engine. | ||
| − | * First tests planned in | + | * First tests planned in December 2020. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left;" | Meas. type !! style="text-align:left;" |Qty !! style="text-align:left;" |Meas. type !! style="text-align:left;" |Qty | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Temperature (mass + flow) || 48 + 78 || 5-Hole probes (2D-3C) || 4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Deformation gauges || 16 || 3-Hole probes (1D-2C) || 13 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Static Pressure || 185 || LDA (2D-2C) || 3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Total Pressure || 14 || Gas analysis (1D) || 11 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Unsteady pressure || 4 || Rotation speed || 2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | BTC || 4 || Optical plug || 1 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Table 2: Main Instrumentation implemented on BEARCAT. | ||
== Type of running to be considered == | == Type of running to be considered == | ||
| Zeile 66: | Zeile 80: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | '''Length''' || 1836 mm || '''Weight''' || 279 kg | |
| − | |||
| − | | Length || 1836 mm || Weight || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | HP turbine || ~ 33000 RPM || OPR || 11 | + | | '''HP turbine''' || ~ 33000 RPM || '''OPR''' || 11 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Output shaft || ~ 23000 RPM || max Cont. || 1410 kW | + | | '''Output shaft''' || ~ 23000 RPM || '''max Cont.''' || 1410 kW |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Torque || ~ 900 Nm || Take-Off || 1563 kW | + | | '''Torque''' || ~ 900 Nm || '''Take-Off''' || 1563 kW |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Turbine Entry T° || > 1100 K || || | + | | '''Turbine Entry T°''' || > 1100 K || || |
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
Table 1: Main characteristics of the Makila 2A1 engine. | Table 1: Main characteristics of the Makila 2A1 engine. | ||
| + | == Indicative Engine Operating Environment == | ||
| + | The engine is operated in ground atmospheric conditions in a dedicated test bench with a dedicated team. | ||
| + | == Expected Availability Date == | ||
| + | First tests are planned in December 2020. | ||
| − | == | + | == Further information == |
| − | + | SAFRAN would be happy to discuss individual requirements with interested parties. | |
| + | Please contact Jean-Louis CHAMPION-REAUD on jean-louis.champion@safrangroup.com. We also welcome any feedback, and would be interested to hear any alternative proposed uses for the facility. | ||
| + | === About SAFRAN Group === | ||
| + | Safran is an international high-technology group, operating in the aviation (propulsion, equipment and interiors), defense and space markets. Its core purpose is to contribute to a safer, more sustainable world, where air transport is more environmentally friendly, comfortable and accessible. Safran has a global presence, with 84,000 employees and holds, alone or in partnership, world or European leadership positions in its core markets. Safran undertakes research and development programs to maintain the environmental priorities of its R&T and Innovation Roadmap. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | + | <br> | |
| + | <hr> | ||
| − | + | <small>EVI-GTI Provides this site to allow members to collaborate in pre-competitive technical areas. EVI-GTI will not be held responsible for loss or corruption of data; inaccuracies in content or actions of members posting to this area. | |
| − | + | </small> | |
Aktuelle Version vom 22. Oktober 2020, 07:11 Uhr
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Introduction
- 2 BEARCAT: A heavily instrumented Turboshaft
- 3 Example Images
- 4 Location
- 5 Engines which can be included in the facility
- 6 Type of modifications to engines
- 7 Probe specifications
- 8 Type of running to be considered
- 9 Indicative Engine Operating Environment
- 10 Expected Availability Date
- 11 Further information
Introduction[Bearbeiten]
BEARCAT (for "Banc d’Essai Avancé pour la Recherche en Combustion et Aérothermique des Turbomachines") is a brand new turboshaft developed by SAFRAN-Tech, the R&D Center of the SAFRAN Group. BEARCAT is based on a MAKILA engine, a turboshaft developed by Safran Helicopter Engines (formerly Turboméca) and powering the H215 and the H225 Airbus Helicopters. BEARCAT has been developed in order to perform fine characterization of aero-thermal phenomena occurring within the combustion chamber and the High Pressure Turbine as well as their interactions. Therefore, BEARCAT differs from a standard test engine by the implementation of metrologies, in order to perform both steady and non-steady flow measurements which will be used to validate CFD codes and models. Therefore, BEARCAT could be used in the framework of fundamental studies, such as aerodynamics, thermics, combustion, acoustics, … as well as applied studies (sensors, materials, technologies, fuels, …). Indeed, thanks to the high degree of instrumentation, BEARCAT allows for the fine characterization of the test conditions and then contributes to the TRL enhancement of the tested technology.
BEARCAT: A heavily instrumented Turboshaft[Bearbeiten]
BEARCAT is based on a MAKILA turboshaft.
The main purpose of BEARCAT is to generate an extensive data base which will be used to validate CFD codes, transient thermal codes, … and models. To address these concerns, it was felt necessary to instrument an engine within the hot temperature / high pressure region, by means of a metrology generally implemented on partial test rig and allowing a fine characterization of local unsteady characteristics of encountered flows. The instrumentation implemented on BEARCAT is summarized in table 2. Special attention was given to the characterization of secondary flows and boundary conditions in terms of temperature (mass and flow) and pressure, in order to characterize the machine performances.
On the other hand, the main flow can be investigated by means of probes implemented at 7 sections, from the Combustor inlet to the HP-Turbine outlet. Each section, or plane, has its own respective instrumentation (indicated in figure 2). Note that only one probe can be implemented at a time. The probe is being automatically traversed into the engine thanks to a versatile device called SYSPAC. This device performs also the data acquisition, independent of the probe type, it performs the data analysis and associates the data to the main engine data collected from the Human Machine Interface.
A perfect tool for fundamental studies[Bearbeiten]
Thanks to the implemented instrumentation BEARCAT is really dedicated to fundamental studies. Indeed, BEARCAT allows for both steady and non-steady flow measurements (velocity, static or dynamic pressure, temperature, chemical species …) coupled with mass temperature or local stress. A classical metrology allows the determination of detailed performances as well as the fine knowledge of the average experimental conditions generating the investigated flows (collected from the HMI). In total, 23 physical access ports es are available on BEARCAT at the level of the Combustor and the HP Turbine, allowing the implementation of a wide range of metrologies, yet existing or to be developed.
A technological platform for Technology Readiness Level (TRL) enhancement[Bearbeiten]
BEARCAT is also well suited for TRL enhancement tests with many advantages. BEARCAT is a real engine with a real and well-known engine environment in terms of thermodynamics, mechanics, vibrations, chemistry …. It gives also the opportunity to eventually quantify the impact of the implemented technology: sensors, equipment, material, fuel, design, materials, process, …. by means of the implemented metrology.
Example Images[Bearbeiten]
Figure 1: Cross-sectional view of a MAKILA 2A1 engine
Figure 2: Partial cross-section of BEARCAT showing the instrumentation implementation.
Location[Bearbeiten]
Tests will be carried out at SAFRAN Group in house facilities in the Safran Helicopter Engine facility located at Bordes F-64510), south of France.
Who the facility will be offered to:
- Sensor manufacturers : new sensor improvement in realistic conditions.
- Universities interested to validate model, computations on a real turboshaft engine by means of dedicated measurements in the fields of aerodynamics, combustion, acoustics, thermics, ...
- Possibility to work in the Framework of EC Projects.
Engines which can be included in the facility[Bearbeiten]
- The rig and the Instrumentation are devoted to BEARCAT. Nevertheless, we are open to new instrumentation development for which BEARCAT would be used for TRL enhancement in engine representative conditions.
Type of modifications to engines[Bearbeiten]
Even any modification of BEARCAT is quickly complicated and expensive, some local modifications in order to implement new type of sensors would be studied very carefully. Don't hesitate to constact us !
Probe specifications[Bearbeiten]
A heavily instrumented turboshaft: 385 measurement points.
- 7 sections (23 physical access ports), from Combustor inlet to HP Turbine outlet, fitted with probes.
- Both steady and unsteady measurements available.
- Well suited to fundamental studies such as CFD validation.
- Well suited to technological works such as TRL enhancement on a real turboshaft engine.
- First tests planned in December 2020.
| Meas. type | Qty | Meas. type | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (mass + flow) | 48 + 78 | 5-Hole probes (2D-3C) | 4 |
| Deformation gauges | 16 | 3-Hole probes (1D-2C) | 13 |
| Static Pressure | 185 | LDA (2D-2C) | 3 |
| Total Pressure | 14 | Gas analysis (1D) | 11 |
| Unsteady pressure | 4 | Rotation speed | 2 |
| BTC | 4 | Optical plug | 1 |
Table 2: Main Instrumentation implemented on BEARCAT.
Type of running to be considered[Bearbeiten]
Please add any other running uses that we have not covered.
| Length | 1836 mm | Weight | 279 kg |
| HP turbine | ~ 33000 RPM | OPR | 11 |
| Output shaft | ~ 23000 RPM | max Cont. | 1410 kW |
| Torque | ~ 900 Nm | Take-Off | 1563 kW |
| Turbine Entry T° | > 1100 K |
Table 1: Main characteristics of the Makila 2A1 engine.
Indicative Engine Operating Environment[Bearbeiten]
The engine is operated in ground atmospheric conditions in a dedicated test bench with a dedicated team.
Expected Availability Date[Bearbeiten]
First tests are planned in December 2020.
Further information[Bearbeiten]
SAFRAN would be happy to discuss individual requirements with interested parties. Please contact Jean-Louis CHAMPION-REAUD on jean-louis.champion@safrangroup.com. We also welcome any feedback, and would be interested to hear any alternative proposed uses for the facility.
About SAFRAN Group[Bearbeiten]
Safran is an international high-technology group, operating in the aviation (propulsion, equipment and interiors), defense and space markets. Its core purpose is to contribute to a safer, more sustainable world, where air transport is more environmentally friendly, comfortable and accessible. Safran has a global presence, with 84,000 employees and holds, alone or in partnership, world or European leadership positions in its core markets. Safran undertakes research and development programs to maintain the environmental priorities of its R&T and Innovation Roadmap.
EVI-GTI Provides this site to allow members to collaborate in pre-competitive technical areas. EVI-GTI will not be held responsible for loss or corruption of data; inaccuracies in content or actions of members posting to this area.